But bioidentical progesterone supplementation can help alleviate digestive issues and naturally boost gut health in multiple ways.
Gut Motility Regulation
Progesterone affects the enteric nervous system, which controls gastrointestinal motility. It modulates smooth muscle activity in the gut through binding to progesterone receptors on the smooth muscle cells of the intestines.
This interaction influences the release of neurotransmitters that either stimulate or inhibit muscle contractions, thus helping to maintain regular bowel movements and preventing constipation.
Studies have shown that progesterone can enhance gastric emptying and transit time in the intestines, which can be beneficial for menopausal women experiencing slowed gastrointestinal motility.
Anti-inflammatory Action
Progesterone exhibits anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reducing the infiltration of inflammatory cells into the gut mucosa.
It acts on the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, a key regulator of inflammation, thereby downregulating the expression of genes involved in the inflammatory response.
This anti-inflammatory effect can help alleviate symptoms of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) and IBS, which can be exacerbated by hormonal changes during menopause.
Modulation of Gut Microbiome
Progesterone has been shown to influence the composition and diversity of the gut microbiome. It promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which play a crucial role in maintaining gut health.
The hormone can alter the gut environment by affecting the production of mucus and antimicrobial peptides, creating conditions that favour the growth of beneficial microbes while inhibiting pathogenic bacteria.
A balanced microbiome is essential for effective digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function.
Enhanced Nutrient Absorption
Progesterone's role in maintaining the integrity of the gut lining is crucial for optimal nutrient absorption.
It supports the tight junctions between intestinal epithelial cells, preventing increased intestinal permeability (leaky gut syndrome), which can lead to malabsorption of nutrients.
By preserving the gut barrier function, progesterone ensures that essential nutrients are efficiently absorbed into the bloodstream, which is vital for menopausal women who require adequate nutrition to support overall health and well-being.
* This information is for general interest only. Every woman is unique. Your results may vary.
Menopause and Hot Flushes
Doctors and Natural Progesterone
Find out what causes this common symptom, and how to get relief
Progesterone supplementation can naturally boost gut health
Hear what doctors have to say about natural progesterone and its benefits
Natural progesterone can be an effective treatment for this serious condition
What happens to hormones at menopause and how can symptoms be treated?
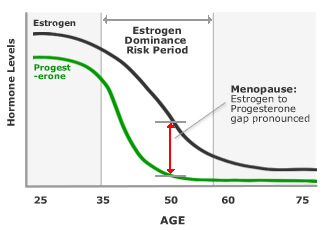
Understand what's behind the increased incidence of oestrogen dominance in the western world
How can a cream deliver progesterone into the body?
What are bioidentical hormones and why are the relevant to your health
Wellsprings offers two varieties of natural progesterone cream. Read on to find out which is best for you
Despite claims to the contrary, Yam Extract does NOT contain progesterone or raise progesterone levels in the body
All information given on this site is for general interest only. Every woman is unique. Your results may vary.